BMW Tests New Humanoid Robot at Spartanburg Plant: What This Means for the Future of Car Manufacturing
Table of Contents
BMW is known for pushing the envelope in car manufacturing, and their latest move is no different. The company recently tested a humanoid robot called Figure 02 at its Spartanburg assembly plant in South Carolina. Developed by California-based robotics company Figure, this isn’t just some high-tech experiment—it’s a potential glimpse into the future of how cars are made.
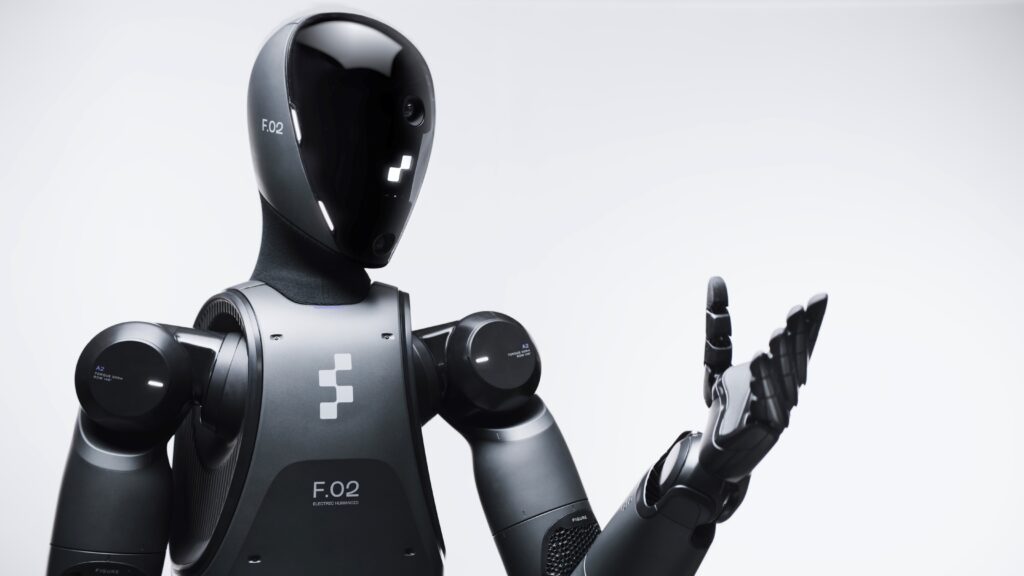

Meet Figure 02: The Robot of Tomorrow
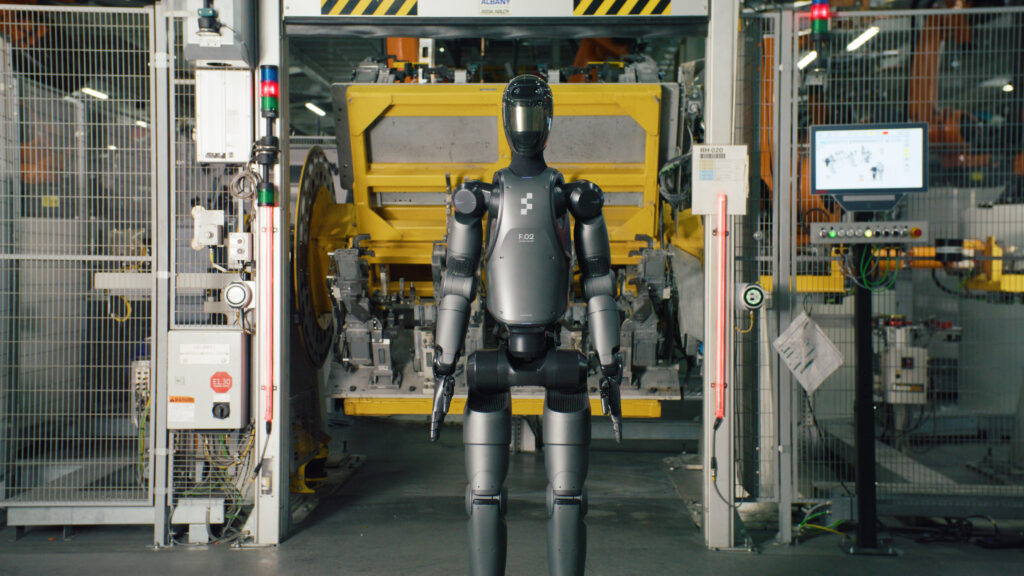
Figure 02 isn’t your average robot. Standing 5’3” tall and weighing 132 pounds, this robot can perform tasks with a level of precision that’s hard to match. It’s equipped with advanced technology, including neural networks that help it translate visual data from its cameras into actions. In simpler terms, it can see what it’s doing and make decisions based on what it sees, just like a human would.
During its test run at the Spartanburg plant, Figure 02 was put to work handling sheet metal parts. This might sound simple, but it’s actually a pretty delicate task that requires both strength and a gentle touch. BMW engineers watched closely as Figure 02 inserted these metal pieces into fixtures, evaluating not just its performance but also how it interacted with its surroundings. The result? BMW was impressed, which is no small feat considering their high standards.
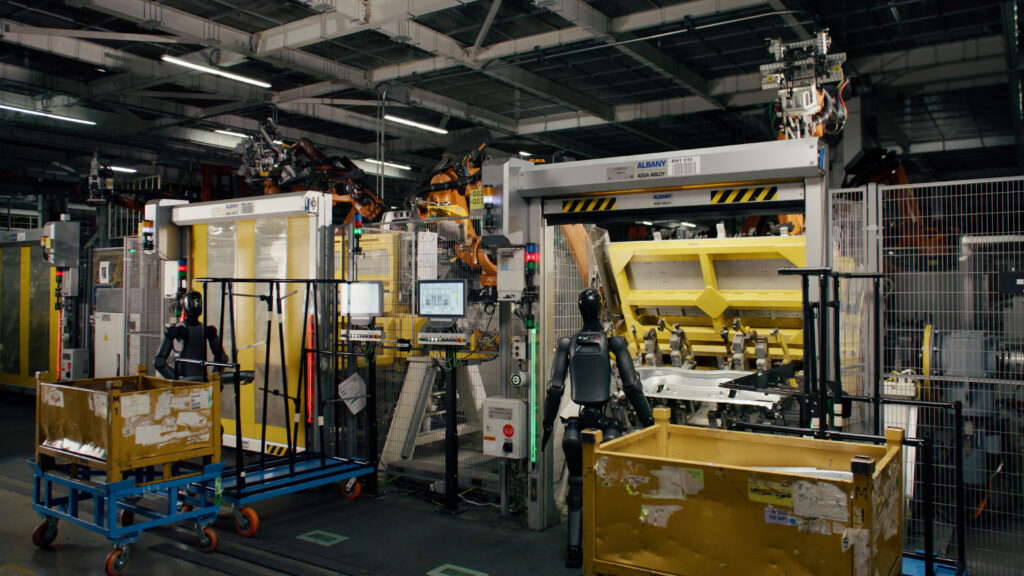
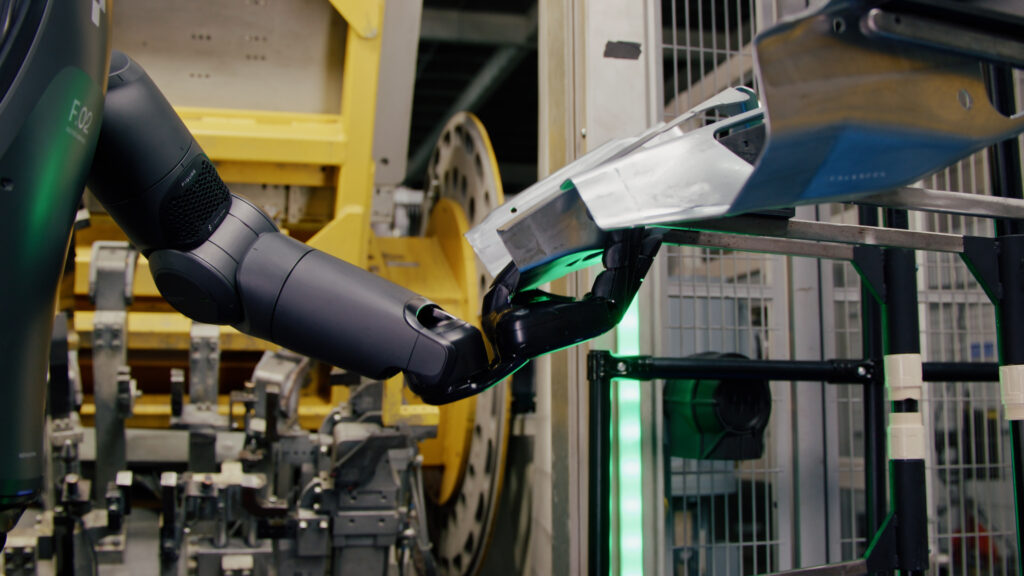
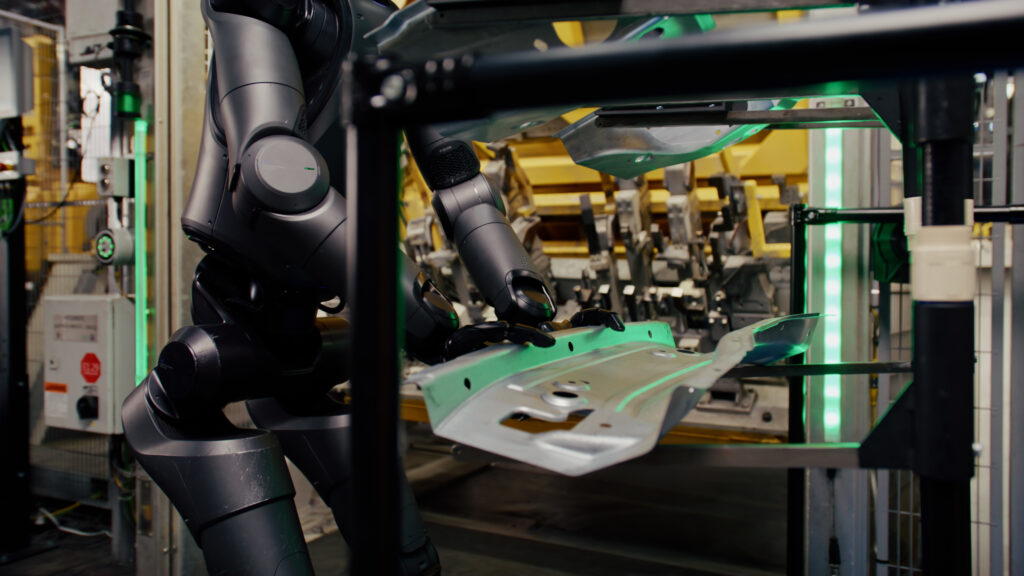



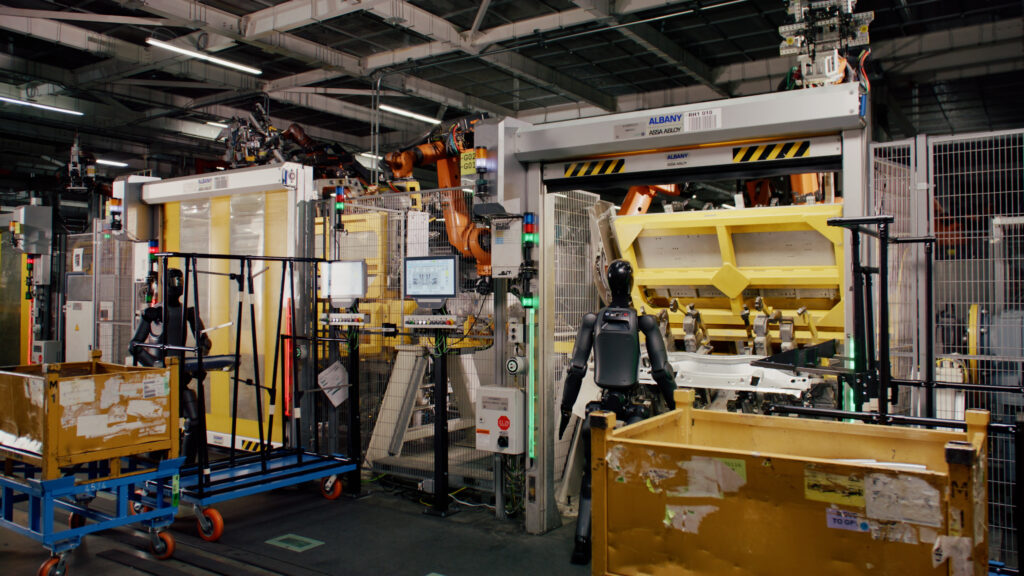
Why Humanoid Robots? Why Now?
So, why is BMW investing in robots like Figure 02? The answer is simple: the future of manufacturing. Car companies around the world are facing labor shortages and looking for ways to make their assembly lines more efficient and safer for workers. Humanoid robots like Figure 02 could be a big part of that solution.
Tasks on the assembly line can be tough on human workers, especially when they involve repetitive motions or awkward positions. Over time, these kinds of jobs can lead to injuries and fatigue. That’s where robots come in. By taking over the physically demanding tasks, robots can free up human workers to focus on more complex and creative work, improving overall productivity and job satisfaction.
The Tech Behind Figure 02
Figure 02 is no ordinary robot. It’s designed with a combination of advanced mobility and dexterity, meaning it can move around and handle objects much like a human. One of its standout features is its hands, which have 16 degrees of freedom—fancy talk for saying they can move in a lot of different ways, just like ours. This allows the robot to perform tasks that require fine motor skills and coordination.
But it’s not just about the hands. Figure 02 is powered by machine learning, a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows the robot to learn and adapt as it works. This means that over time, the robot can get better at its job, making fewer mistakes and working more efficiently. Plus, it can run for up to five hours on a single charge, making it a reliable addition to any assembly line.
What’s Next for Figure 02 and BMW?
Even though the test at Spartanburg went well, BMW is taking things slow. There are currently no plans to permanently station Figure 02 robots at the plant, and there’s no timeline for when that might happen. BMW is still in the early stages of figuring out how robots like Figure 02 could fit into their long-term plans.
That said, the potential is huge. If Figure 02 and other robots like it prove their worth, we could see them becoming a common sight on assembly lines around the world. For BMW, this would be part of their broader “iFactory” vision, which focuses on making car production more efficient, sustainable, and digitalized.
The Big Picture: Robots in the Auto Industry
BMW isn’t the only car company exploring the use of robots. Other automakers, like Tesla, Honda, and Mercedes, are also looking into how robots can help them build cars more efficiently and safely. The push towards automation is driven by a few key factors, including labor shortages, the need to cut costs, and the desire to reduce workplace injuries.
But there’s also a bigger picture here. As populations age and fewer people are available for physically demanding jobs, robots could fill in the gaps. In fact, some experts predict that robots could eventually take on millions of jobs that humans either don’t want or can’t do.
The Road Ahead
The test of Figure 02 at BMW’s Spartanburg plant is a small step, but it could lead to big changes in the way cars are made. If robots like Figure 02 can take over the tough, repetitive tasks, they could make assembly lines safer and more efficient. And while it might be a while before we see these robots in full-time action, the wheels are definitely in motion.
For gearheads and industry watchers, this is an exciting development. It’s not just about building cars faster—it’s about shaping the future of manufacturing. So keep an eye on Figure 02 and the robots that come after it. They might just be the next big thing in the auto industry.
Want to read more articles like this?
Join the PowerNation Email NewsletterRead More from PowerNation
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions off, selected
- default, selected
This is a modal window.








